Paper types and their characteristics
Modern paper manufacturing employs many processes. From classic cellulose paper to environmentally friendly recycled paper through to premium products, each type offers its advantages. The differences lie not only in softness, absorbency and strength, but also in production costs and environmental impacts. The choice of paper type therefore depends heavily on the area of application and quality requirements. In our online shop, you’ll find various articles for each type.
Recycled Paper
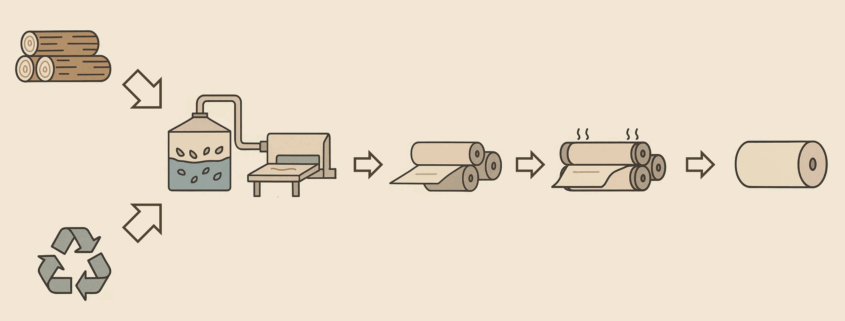
Recycled paper is manufactured from reused paper materials. Waste paper is shredded, cleaned and processed into new paper. Through recycling, fewer resources are needed, waste is reduced and forests can be protected. However, there are quality differences. The recycled product is often less soft, less absorbent and may show colour variations. The complex cleaning process also requires chemicals and energy, making production more complex and sometimes more expensive than conventional paper.
Cellulose Paper
Classic cellulose paper is the most widespread and is manufactured from wood fibres using the traditional wet-forming process. The cellulose fibres are dispersed in water, formed into sheets, pressed and dried. It offers high strength, brightness and a smooth surface. The advantages are consistent quality and efficient mass production. Disadvantages include dependence on wood resources with corresponding sustainability concerns as well as lower softness and absorbency. Besides the classic drying process for cellulose paper, there are three other forms of paper finishing.
Air-Laid Paper
Air-laid paper is manufactured using air instead of water. Wood fibres are mixed with binding agents and evenly distributed through air streams. The result is a product with very good absorbency and high durability. These properties make air-laid paper ideal for high-quality towels and special wipes. However, this method has its price. Specialised machinery and an energy-intensive process lead to higher costs than conventional paper manufacturing processes.
Through-Air Drying Paper (TAD)
TAD paper is created when wet paper is passed through with hot air instead of mechanical pressing. The fibres are arranged before drying, which produces high softness, good strength and absorbency in the paper. These properties make it popular in the high-quality sanitary sector. The disadvantages include higher energy consumption, greater environmental impact and complex production facilities.
Through-Air Embossing Paper (TAE)
Through-Air Embossing (TAE) technology combines air drying and mechanical wet pressing in one process step. Here, embossing is crucial. It occurs directly during drying, creating a uniform texture and more volume. TAE paper thus has better absorbency, increased softness, appealing appearance and less linting. Perfect for premium toilet paper. Disadvantages are the high investment costs and increased energy consumption. These increase production costs and environmental impact.